Pricing psychology is all about using the way products are priced to influence a customer’s buying choices or their spending habits. It’s a strategy designed to tap into the emotions of customers to increase sales, all without changing the actual prices of products.
Have you ever gone grocery shopping with a strict list and a budget, but somehow found yourself filling your cart with stuff you hadn’t planned to buy? Most of the time, this results from the store’s superb pricing psychology strategy that gets you hooked!
In this article, we’ll dive deeper into the world of price psychology and uncover why it’s so incredibly effective. After that, we’ll provide you with 11 practical tips and examples to help you boost sales in your e-commerce store. So, let’s delve right in!
Pricing Psychology And Why It Works In WooCommerce
To put it simply, psychological pricing is all about influencing consumer behavior to increase spending. Pricing, marketing, and sales work together to create an enticing offer that draws in customers and makes a product so appealing that the customer can’t resist buying it.
Think of it this way: if you stumbled upon an incredible, time-sensitive deal for a valuable product, would you just walk away? Probably not. Chances are, you’d buy this straight away, believing that you had saved a ton of money.
This is precisely how pricing psychology works—customers are drawn in and led to believe they have won as a result of your offer. In return, you increase your sales without having to adjust individual prices.

It’s not really a new concept. Savvy businesspeople have long influenced consumer behavior by using pricing approaches to influence purchasing decisions.
While it may seem like pricing tricks are everywhere, that doesn’t mean they’re unimportant.
Actually, they play such a big role in how prices, marketing, and sales work that it’s essential for you to understand how they work.
Why are they effective for boosting sales?
The simplest answer is that it triggers emotions and meets fundamental human wants.
Imagine, what do shoppers want the most? Saving money and receiving value, right?

Psychological pricing takes advantage of the fact that people don’t always have a clear idea of what something should cost. This is why it’s effective: most consumers think they’re getting a good deal when they pay less than the perceived norm or when they compare prices to similar items.
Additionally, psychological pricing relies on subtle tweaks to trick the mind, making it even more powerful. For instance, consider charm pricing. When you price your product at $3.99 instead of $4, customers tend to remember the $3 part, making it seem like a better deal.
11 Pricing Psychology Tips To Help You Sell More
Setting the right prices for your products is a powerful move that requires careful planning. When done right, it can be a great tool for elevating your brand and driving sales. In fact, according to McKinsey & Company, pricing is by far the biggest tool for earnings improvement.
But first, before we dive into the techniques of psychological pricing, it’s essential to grasp that pricing isn’t just about manipulating numbers. It often requires additional research, thoughtful design, and marketing strategies to be effective.
Now, let’s talk about strategies:
1. Avoid BIG FONTS
Did you realize that a price’s appearance might affect how customers perceive it? For example, big fonts can make it seem like the product is expensive.
According to Coulter and Coulter (2005), the way a discounted offer is presented may have a greater impact on a customer’s likelihood to purchase it than the amount of the discount. This means that the text’s font, color, and size are all important factors in how buyers interpret sales messaging.
Have you noticed how the second example seems less intimidating? Our brains tend to link the price tag with a lower cost automatically.
When you display the discounted price in a smaller font compared to the original price, it’s more likely to encourage a purchase. This is because we tend to associate smaller text with lower prices.
2. Get rid of the $igns
In a study, Cornell University researchers discovered that the presence or absence of the “$” symbol before the price had a substantial impact on how much customers spend at any given time.
This is because the dollar sign often triggers “the pain of paying” among consumers.
The uncomfortable feelings people go through when they have to pay for products or services are referred to as the “pain of paying.”
For example, when you make a payment with cash, you feel the pain of paying way more because cash physically represents hard-earned money. Therefore, when we hand cash to the cashier, we are experiencing a greater loss than when we pay via cards.
The dollar sign ($) carries a similar weight. Since this symbol is closely tied with cash, it triggers the “pain of paying” more than prices displayed without the dollar sign.
3. Offer BOGO deals
Surprisingly, not many people are aware of this, but many stores these days use a common example of pricing strategy by offering “Buy One, Get One” deals.
Of course, businesses love to offer BOGO discounts because they know it can tempt more customers to buy without them feeling like they’re spending too much. But did you know that the magic behind this trick actually lies in the idea of getting something for free?
In his book “Predictably Irrational,” Dan Ariely asserts that when a seller offers something for free, people alter their behavior patterns and become more compliant. Free is more than just a price indicator. It’s a really intense emotional response that frequently leads people to buy tight jeans and bring home meaningless key chains merely to obtain an extra pair for free.
If you’re looking for a way to incorporate this strategy into your WooCommerce store, we highly recommend checking out Advanced Coupons’ Prices Premium plugin.
This powerful plugin extends WooCommerce’s coupon capabilities in various ways. For instance, it lets you offer BOGO deals, automate coupons with cart conditions, shipping discounts, URL coupons, store credit, and many more.
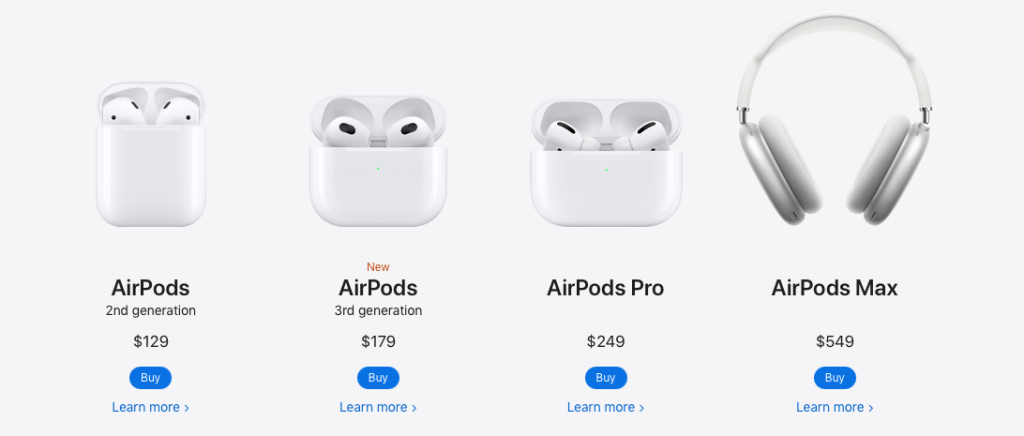
4. Minus one (charm pricing)
You have probably already experienced this price psychology as a customer. Ever encountered prices like $1.99 or $14.99 in the past?
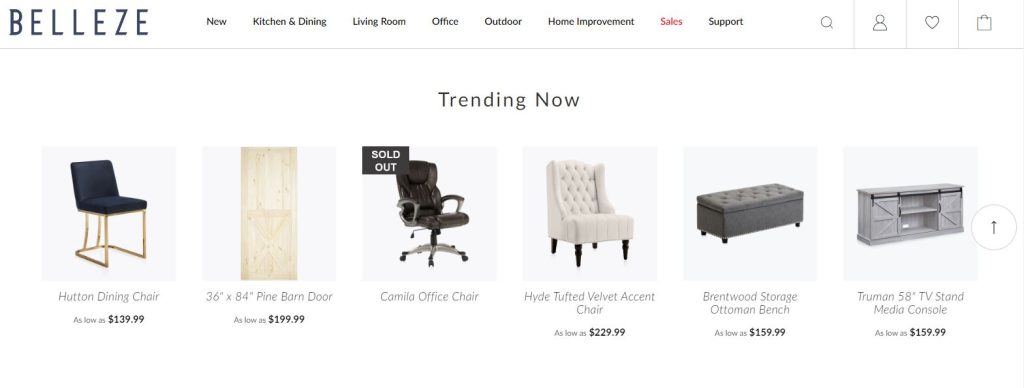
Charm pricing refers to reducing a product’s left digit by one and lowering its cost by one cent in order to increase its customer desirability. Check out Belleze’s catalog, for example:
According to studies, by reducing even a single cent, our brains are automatically tricked into believing that the product costs less.
5. Use odd numbers (odd-even pricing)
We can use the last digit of a product or service price in the pricing approach known as odd-even pricing.
In this strategy, prices with odd number endings, like $99 or $19.95, are deemed to persuade more customers as opposed to prices with even number endings, like $100 or $20.
The psychology underlying the practice depends on how much attention customers give to a price’s first number. More so than the overall price, that first figure frequently shapes a consumer’s sense of a product’s value.
So, for instance, if your product costs $20, price it at $19.95. Customers will start to think of the price as cheaper as they will associate it with ‘1’.
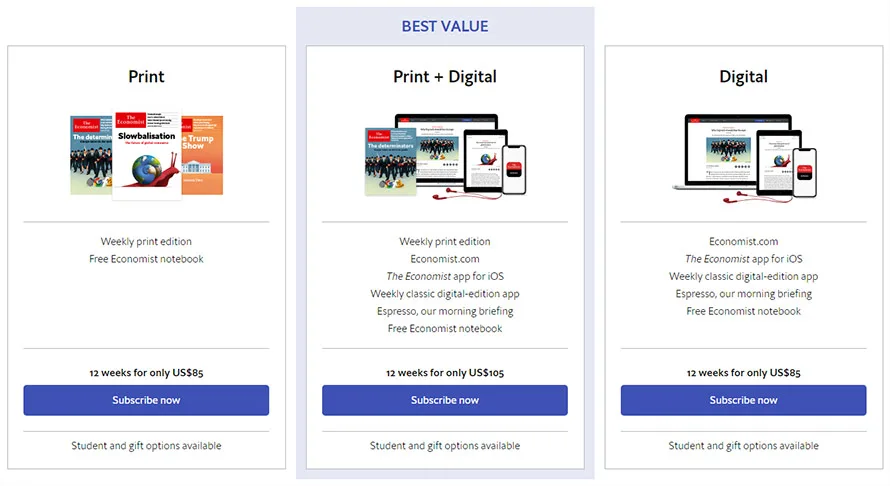
6. Anchor prices
Another common psychological trick you can try is anchoring your prices.
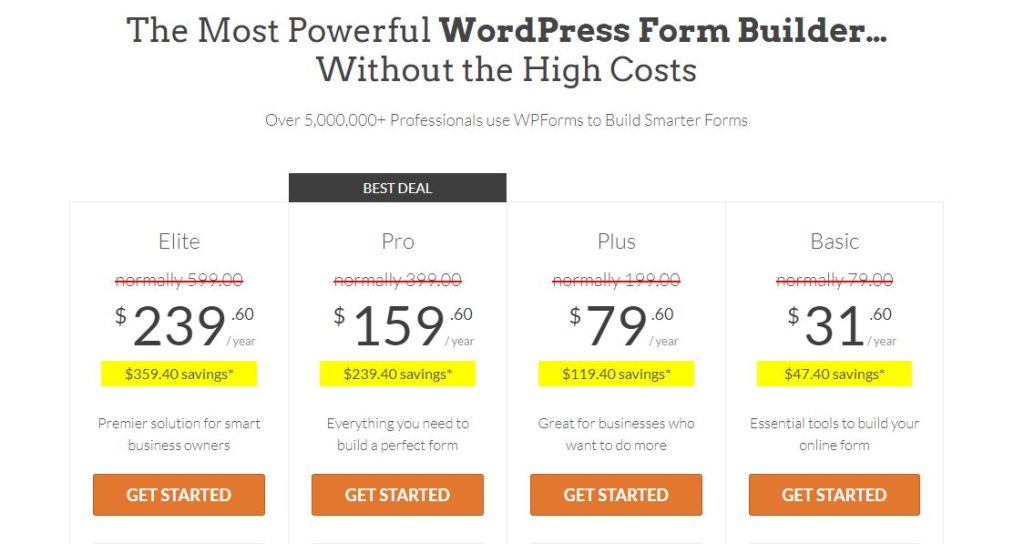
Price Anchoring refers to the practice of establishing a pricing point that buyers can use as a reference point when making purchase decisions. A great illustration of this strategy would be WPForm’s pricing:
Whether you work in software or not, developing a tiered pricing strategy that offers various iterations of a core product at multiple rates is the simplest way to apply price anchoring. By doing so, you may instantly incorporate your anchor prices and benefit from the multi-price thinking.
If you decide against doing that, you might also display the prices of your rivals on your pricing website. This provides a framework for your customers to evaluate your solution. However, note that it also has the danger of exposing them to other options.
7. Set flat rates
The flat-rate bias is the tendency of customers to choose flat rates over pay-per-use choices, even when the costs are equal to or higher when taking into account actual usage.
According to Ariyh’s study, 23% of respondents still opted for a flat rate even though it costs 20% more than pay-per-use. Similarly, 15% of B2B buyers still chose flat rates even when they were 50% pricier.
The psychology behind the bias is the fact that flat rates are simpler and more convenient. For B2B, especially, buyers prefer flat rates for two main reasons:
- It reassures customers that there won’t be any possible overcharging.
- It eliminates the hassle of monthly payments (or periods of billing).
8. Arrange pricing orders
Have you noticed that in some restaurants, menus are arranged in descending order according to price? This is an example of a price order.
Research shows that decreasing the order in which a price list is displayed, as on a menu, can help increase sales. This is because many people tend to select the more expensive items.
The reason behind this is primarily influenced by the natural inclination to fear loss.
For instance, when presented with more expensive options first, we are more likely to believe that the quality will decrease as we scroll down the list. Of course, this thought process would not have occurred if the prices had been listed in ascending order.
9. Compare prices
If you’re into a more aggressive psychological approach, you might want to consider this next tip:
Comparative pricing basically entails simultaneously presenting two products that are comparable but drastically raising the price of one of the products.
Here, buyers are playing a psychological game of choice where they must decide between two identical but price-different products.
And when given a choice between a standard and premium option, consumers are more likely to choose the premium option if the price is presented as the cost of an upgrade from the standard option rather than as a separate expense.
10. Prestige pricing
While prestige pricing is quite the opposite of discounting, it can likewise boost sales if done correctly.
Prestige pricing is a method of setting prices that leverages higher costs to imply superiority and quality. In this approach, customers are expected to pay more for the correct image and won’t look into whether the price fairly reflects the value.
By convincing customers that there is an added value for the price, prestige pricing gives businesses a psychological marketing edge. It also capitalizes on the buyer’s perception that a brand’s product is of higher quality than its rivals since it’s more expensive.
It’s important to remember, however, that this strategy can work against you if your product lacks anything remarkable or distinctive. Likewise, it’s essential to establish a unique branding first.
11. Add in a decoy
The decoy effect is a phenomenon where buyers frequently alter their selections when given a third option. Imagine this: option A is cheaper than option B.
As a consumer, would you be inclined to purchase option B? Without any added value or considerations, of course, we’d opt for option A as it costs less. But what if there’s option C?
In this scenario, the decoy effect eliminates choice A and tempts customers to think twice about option B, the ‘tradeoff’.
The decoy effect works because our brain automatically rejects the cheapest alternative since it feels inferior to the other choices, whether or not they actually fit our needs.
When it comes to the most expensive of the three, our subconscious mind intervenes and convinces us that the extra features are not necessary or worth the additional cost.
So, we end up choosing the middle ground.
Conclusion: Pricing Psychology Can Help You Sell More Stuff!
The study of consumer behavior is used as a springboard by pricing psychology to sway daily purchasing behaviors. As a business owner, you can increase your sales effortlessly by analyzing how specific figures, phrasing, and visuals connected to products resonate with consumers.
In this article, we shared 11 pricing psychology tips that can help you boost revenue. To recap, they are:
- Avoid big fonts
- Get rid of the $ sign
- Offer BOGO deals
- Use charm pricing
- Use odd-even pricing
- Anchor prices
- Set flat rates
- Arrange pricing orders
- Compare prices
- Use prestige pricing
- Add in a decoy
You may also use Advanced Coupons’ All-In-One plugin to further enhance your store. This will not only help you increase sales but also improve customer loyalty and retention!
Do you have any questions about pricing psychology? Send us a message or let us know in the comment box down below!